Allergy 家用洗涤剂破坏屏障完整性引起小鼠和人体皮肤炎症
发布日期:2023-10-30
——浙大迪迅 译
背景:上皮屏障损伤与许多皮肤和粘膜炎症性疾病有关。使用人类上皮细胞的气液界面培养物,洗涤剂已被证明在体外影响上皮屏障功能。
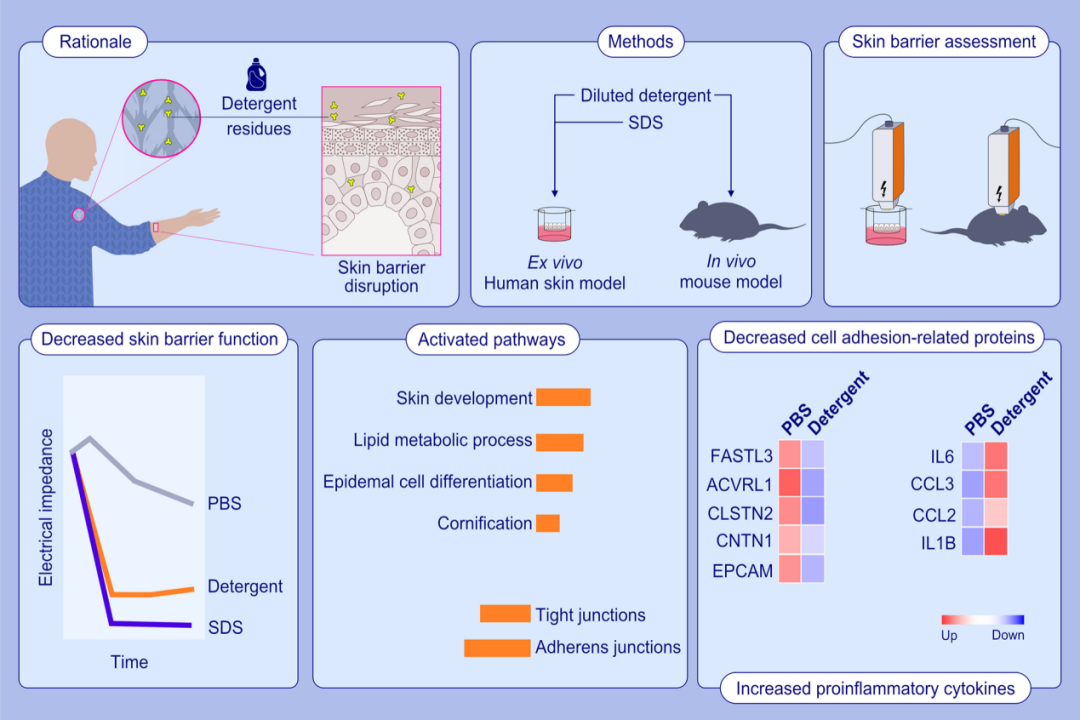
方法:用两种不同稀释度的家用洗涤剂处理C57BL/6小鼠背部皮肤。用电阻抗谱(EIS)和经皮失水(TEWL)测量方法评估洗洁剂处理4 h后的屏障功能。对皮肤活检样本进行RNA测序(RNA-seq)和靶向多重蛋白质组学分析。研究了洗涤剂和十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)对离体人体皮肤6小时的处理效果。
结果:与未处理的皮肤相比,洗涤剂处理的皮肤显示出显着的EIS降低和TEWL增加,对EIS的敏感性和剂量反应相对较高。RNA-seq结果显示,对皮肤屏障完整性至关重要的几个基因表达减少,如紧密连接蛋白和粘附连接蛋白。相反,角化、脂质代谢过程和表皮细胞分化上调。蛋白质组学分析显示,洗涤剂处理后,细胞粘附相关蛋白如上皮细胞粘附分子和接触蛋白-1普遍下调,促炎蛋白如白细胞介素6和白细胞介素1 β上调。在离体人体皮肤模型中,洗涤剂和SDS均导致EIS值显著降低。
结论:本研究表明,洗涤剂及其主要成分SDS对人体内和离体皮肤的表皮屏障有损伤作用。每天接触洗涤剂可能会导致皮肤屏障破坏,并可能导致特应性疾病的发展。
原始出处
Allergy
DOI: 10.1111/all.15891
Abstract:
Background:Epithelial barrier impairment is associated with many skin and mucosal inflammatory disorders. Laundry detergents have been demonstrated to affect epithelial barrier function in vitro using air–liquid interface cultures of human epithelial cells.
Methods:Back skin of C57BL/6 mice was treated with two household laundry detergents at several dilutions. Barrier function was assessed by electric impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and transepidermal water loss (TEWL) measurements after the 4 h of treatments with detergents. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and targeted multiplex proteomics analyses in skin biopsy samples were performed. The 6-h treatment effect of laundry detergent and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) was investigated on ex vivo human skin.
Results:Detergent-treated skin showed a significant EIS reduction and TEWL increase compared to untreated skin, with a relatively higher sensitivity and dose–response in EIS. The RNA-seq showed the reduction of the expression of several genes essential for skin barrier integrity, such as tight junctions and adherens junction proteins. In contrast, keratinization, lipid metabolic processes, and epidermal cell differentiation were upregulated. Proteomics analysis showed that the detergents treatment generally downregulated cell adhesion-related proteins, such as epithelial cell adhesion molecule and contactin-1, and upregulated proinflammatory proteins, such as interleukin 6 and interleukin 1 beta. Both detergent and SDS led to a significant decrease in EIS values in the ex vivo human skin model.
Conclusion:The present study demonstrated that laundry detergents and its main component, SDS impaired the epidermal barrier in vivo and ex vivo human skin. Daily detergent exposure may cause skin barrier disruption and may contribute to the development of atopic diseases.
First Author:
Arturo O. Rinaldi
Corresponding author:
Yasutaka Mitamura
Correspondence: Swiss Institute of Allergy and Asthma Research (SIAF), University of Zurich, Herman-Burchard Strasse 9, CH-7265 Davos, Wolfgang, Switzerland.
Email: yasutaka.mitamura@siaf.uzh.ch
Allergy
[IF: 14.71]
Household laundry detergents disrupt barrier integrity and induce inflammation in mouse and human skinDOI: 10.1111/all.15891
Abstract:
Background:Epithelial barrier impairment is associated with many skin and mucosal inflammatory disorders. Laundry detergents have been demonstrated to affect epithelial barrier function in vitro using air–liquid interface cultures of human epithelial cells.
Methods:Back skin of C57BL/6 mice was treated with two household laundry detergents at several dilutions. Barrier function was assessed by electric impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and transepidermal water loss (TEWL) measurements after the 4 h of treatments with detergents. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and targeted multiplex proteomics analyses in skin biopsy samples were performed. The 6-h treatment effect of laundry detergent and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) was investigated on ex vivo human skin.
Results:Detergent-treated skin showed a significant EIS reduction and TEWL increase compared to untreated skin, with a relatively higher sensitivity and dose–response in EIS. The RNA-seq showed the reduction of the expression of several genes essential for skin barrier integrity, such as tight junctions and adherens junction proteins. In contrast, keratinization, lipid metabolic processes, and epidermal cell differentiation were upregulated. Proteomics analysis showed that the detergents treatment generally downregulated cell adhesion-related proteins, such as epithelial cell adhesion molecule and contactin-1, and upregulated proinflammatory proteins, such as interleukin 6 and interleukin 1 beta. Both detergent and SDS led to a significant decrease in EIS values in the ex vivo human skin model.
Conclusion:The present study demonstrated that laundry detergents and its main component, SDS impaired the epidermal barrier in vivo and ex vivo human skin. Daily detergent exposure may cause skin barrier disruption and may contribute to the development of atopic diseases.
First Author:
Arturo O. Rinaldi
Corresponding author:
Yasutaka Mitamura
Correspondence: Swiss Institute of Allergy and Asthma Research (SIAF), University of Zurich, Herman-Burchard Strasse 9, CH-7265 Davos, Wolfgang, Switzerland.
Email: yasutaka.mitamura@siaf.uzh.ch
 hth官方网页版中国有限公司
hth官方网页版中国有限公司

