Release date:2023-01-11
JACI
[IF:14.290]
Filaggrin loss-of-functionmutations are associated with persistence of egg andmilk allergyDOI: org/10.1016/j.jaci.2022.05.018
Abstract:
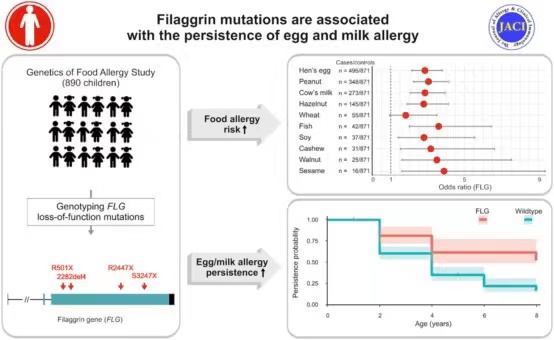
Background: A genetic defect in the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin (FLG) plays a major role in the etiology of eczema and associatedallergic airways diseases.However, it is still controversial to what extend loss-of-function (LOF)mutations in FLG contribute to the development and persistence of food allergies.
Objectives: This study tested association of FLG LOF mutations with allergic reactions to diverse foods and investigated their potential effect on the persistence of early food allergies.
Methods: This study recruited 890 children with challengeproven food allergy for the German Genetics of Food Allergy Study (GOFA). Longitudinal data were available for 684 children. All children were clinically characterized, including their allergic responses to specific foods, and genotyped for the 4 most common LOF mutations in FLG; R501X,2282del4,R2447X, and S3247X. Associations between FLG mutations and food allergies were analyzed by logistic regression using the German Multicenter Allergy Study cohort as the control population.
Results: FLG mutations were associated with allergies to diverse foods including hen’s egg (HE), cow’s milk (CM), peanut,hazelnut, fish, soy, cashew, walnut, and sesame with similar risk estimates. Effects remained significant after adjusting for the eczema status. Interestingly, FLG mutations increased the risk of a persistent course of HE and CM allergy.
Conclusions: Using the gold standard for food allergy diagnosis,this study demonstrates that FLG LOF mutations confer a risk of any food allergy independent of eczema. These mutations predispose to the persistence of HE and CM allergy and should be considered in the assessment of tolerance development.
First Author:
Birgit Kalb
Correspondence:
Max-Delbruck-Center, Robert-Rossle-Strasse 10, 13092 Berlin, Germany
2023-01-04 Article
 hth官方网页版中国有限公司
hth官方网页版中国有限公司
