Release date:2019-04-30
JACI
[IF:13.1]
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: A fibrosing alveolitis produced by inhalation of diverse antigenshttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2018.09.040
Abstract:
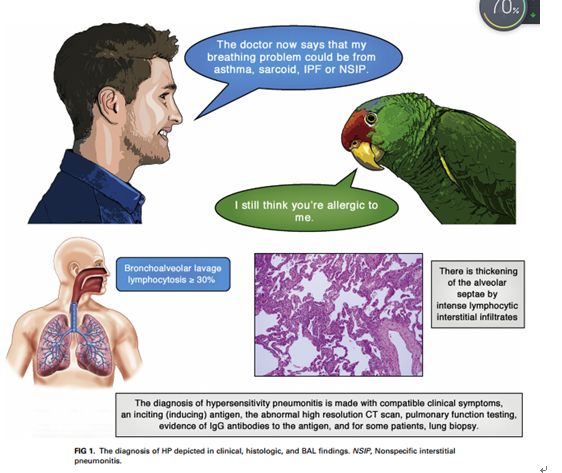
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is a TH1 lymphocyte–biased fibrosing alveolitis caused by antigens ranging from avian excreta, fungi, thermophilic bacteria, and protozoa to reactive chemicals found in the workplace. Mimicking a viral syndrome, acute exposures to inciting antigens cause abrupt onset of nonproductive cough, dyspnea, and chills with arthralgias or malaise usually from 4 to 8 hours later so that the temporal relationship between antigen exposure and symptoms might be unsuspected. The histology of HP reveals prominent lymphocyte infiltrates that thicken the alveolar septa with poorly formed granulomas or giant cells. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid demonstrates greater than 20% lymphocytes in nearly all patients. Abnormalities on high-resolution computed tomographic examinations range from nodular centrilobular opacities in acute/subacute disease to increased reticular markings and honeycombing fibrosis, which typically are predominant in the upper lobes, in patients with advanced disease. Descriptors include “mosaic” attenuation and ground-glass opacities. Repeated episodes can result in nodular pulmonary infiltrates and suspected nonspecific interstitial pneumonia or idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clinicians require a high level of suspicion to make an early diagnosis of HP before extensive pulmonary fibrosis or restrictive lung disease has occurred.an expert panel of the American Thoracic Society commented that, ‘‘For patients with suspected interstitial lung disease in whom BAL is performed, we suggest that lymphocyte subset analysis NOT be a routine component of BAL cellular analysis.’’ What constitutes a ‘‘high level of confidence’’ in diagnosis is a matter of debate. In the absence of a diagnostic test, the diagnosis is made with compatible clinical symptoms, an inciting (inducing) antigen, an abnormal high-resolution computed tomographic (CT) scan, pulmonary function testing, evidence of IgG antibodies to the antigen, and, for some patients, lung biopsy.
Authors:
Paul A. GreenbergerMD
2019-4-16 Review
 hth官方网页版中国有限公司
hth官方网页版中国有限公司
