Release date:2019-06-06
JACI
[IF:13.1]
Broad IgG repertoire in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps regulates proinflammatory IgE responses
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2019.02.001
Abstract:
Background
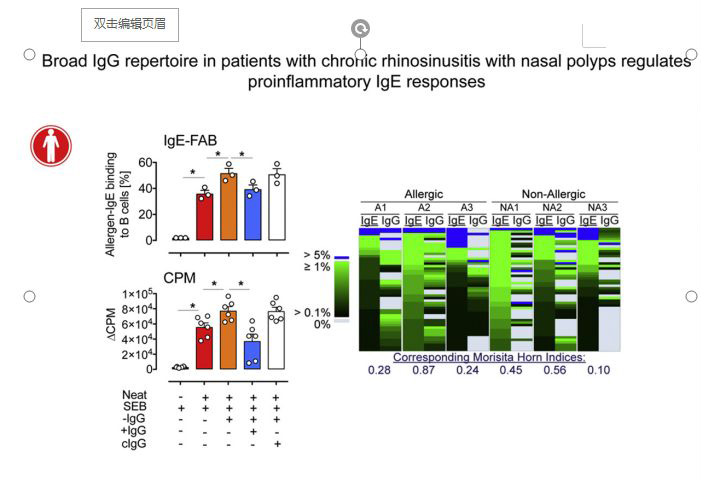
Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) is often characterized by local production of polyclonal IgE idiotypes. Although tissue IgE concentrations can be in the range of several thousand kilounits per liter, the regulatory mechanisms by which IgE-mediated inflammation is controlled in patients with nasal polyps are not well understood.
Objective
We sought to determine whether locally induced IgG antibodies in patients with nasal polyps can inhibit an IgE-mediated proallergic response.
Methods
Nasal polyp homogenates were collected from patients with grass pollen allergy with CRSwNP and nonallergic control subjects. IgE levels were measured using the Immuno Solid-phase Allergen Chip assay. IgE-containing nasal polyp homogenates with or without IgG depletion were evaluated for their capacity to promote IgE-facilitated allergen presentation, basophil activation, and histamine release. Local IgE and IgG repertoires were evaluated using Immunoglobulin 454 sequencing.
Results
We show that IgG plays a key role in controlling IgE-mediated inflammatory responses in patients with nasal polyps. Depletion of IgG from nasal homogenates resulted in an increase in CD23-mediated IgE-facilitated allergen binding to B cells but also enhanced FcεRI-mediated allergen-driven basophil activation and histamine release. A similar response was observed in relation to specific IgE antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins. The capacity of IgG in nasal polyps to limit IgE-mediated inflammation is based on the fact that IgG repertoires widely share the antigen targets with the IgE repertoires in both allergic and nonallergic subjects.
Conclusion
Polyclonal IgE idiotypes in patients with CRSwNP are functional, promote IgE-mediated proallergic inflammation, and are partially antagonized by corresponding IgG idiotypes. This is most likely due to the fact that IgE and IgG clonotypes are widely shared in patients with nasal polyps.
All Authors:
Mohamed H. Shamji Irene Thomsen Janice A. Layhadi Jasper Kappen Gabriële Holtappels Umit Sahiner Amy Switzer Stephen R. Durham Oliver Pabst
Claus Bachert∗
2019-5-6 Article
 hth官方网页版中国有限公司
hth官方网页版中国有限公司
