Release date:2019-06-06
JACI
[IF:13.1]
Indoor microbial communities: Influence on asthma severity in atopic and nonatopic children
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.11.027
Abstract:
Background
Allergic and nonallergic asthma severity in children can be affected by microbial exposures.
Objective
We sought to examine associations between exposures to household microbes and childhood asthma severity stratified by atopic status.
Methods
Participants (n = 196) were selected from a cohort of asthmatic children in Connecticut and Massachusetts. Children were grouped according to asthma severity (mild with no or minimal symptoms and medication or moderate to severe persistent) and atopic status (determined by serum IgE levels). Microbial community structure and concentrations in house dust were determined by using next-generation DNA sequencing and quantitative PCR. Logistic regression was used to explore associations between asthma severity and exposure metrics, including richness, taxa identification and quantification, community composition, and concentration of total fungi and bacteria.
Results
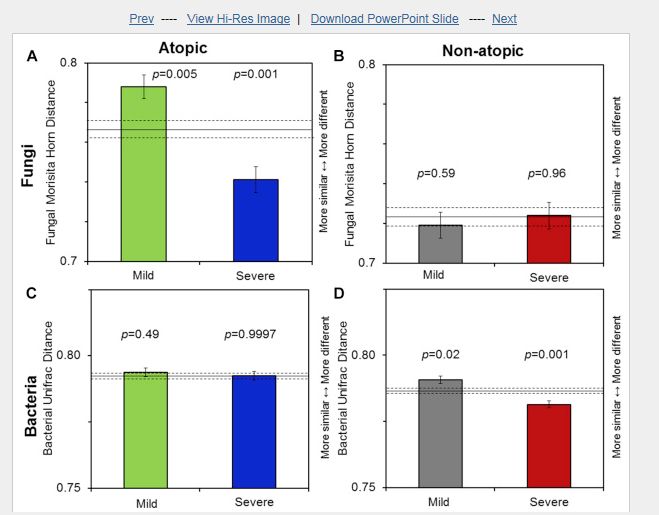
Among all children, increased asthma severity was significantly associated with an increased concentration of summed allergenic fungal species, high total fungal concentrations, and high bacterial richness by using logistic regression in addition to microbial community composition by using the distance comparison t test. Asthma severity in atopic children was associated with fungal community composition (P = .001). By using logistic regression, asthma severity in nonatopic children was associated with total fungal concentration (odds ratio, 2.40; 95% CI, 1.06-5.44). The fungal genus Volutella was associated with increased asthma severity in atopic children (P = .0001, q = 0.04). The yeast genera Kondoa might be protective; Cryptococcus species might also affect asthma severity.
Conclusion
Asthma severity among this cohort of children was associated with microbial exposure, and associations differed based on atopic status.
All Author:
Karen C. Dannemiller Janneane F. Gent Brian P. Leaderer Jordan Peccia
2019-5-2 Artical
 hth官方网页版中国有限公司
hth官方网页版中国有限公司
