Release date:2019-04-15
Allergy
[IF:6.048]
Intranasal administration of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG prevents birch pollen-induced allergic asthma in a murine model DOI: 10.1111/all.13502
Abstract:
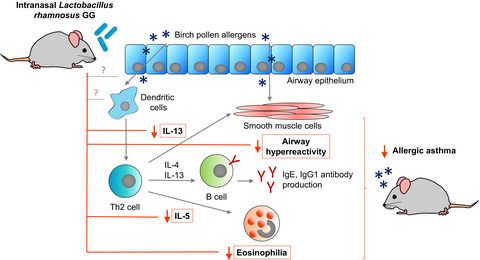
Background: There is an increasing interest in targeted application of probiotic bacteria for prevention and treatment of airway diseases, including allergies. Here, we investigated the beneficial effects of preventive intranasal treatment with probiotics Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and L. rhamnosus GR-1 in a mouse model of allergic asthma.
Methods: L. rhamnosus was administered intranasally eight times on days 1-4 and 8-11 at 5x108 CFU/dose, followed by a two-week asthma induction protocol with birch pollen extract on alternating days. Effects of preventive treatment were analyzed based on serum antibody levels, bronchoalveolar lavage cell counts, lung histology, lung cytokine levels and airway hyperreactivity. Colonization and translocation of L. rhamnosus was assessed by bacterial cell counts in nasal mucosa, fecal samples, cervical lymph nodes and blood. Binding of fluorescent L. rhamnosus to fixed murine nasal mucosal cells and airway macrophages was visualized by fluorescence microscopy.
Results: Transient colonization of the murine upper airways by L. rhamnosus GG was demonstrated and was approximately ten times higher compared to L. rhamnosus GR-1.Marked binding of fluorescent L. rhamnosus GG to murine nasal mucosal cells and airway macrophages was visualized. Preventive treatment with L. rhamnosus GG (but not L.rhamnosus GR-1) resulted in a significant decrease in bronchoalveolar lavage eosinophil counts, lung interleukin-13 and interleukin-5 levels, and airway hyperreactivity. A tendency towards a decrease in serum Bet v 1-specific IgG1was likewise observed.
Conclusion: Intranasally administered L. rhamnosus GG prevents the development of cardinal features of birch pollen-induced allergic asthma in a strain-specific manner.
First Author:
Irina Spacova
Correspondence:
University of Antwerp, Department of Bioscience Engineering,Groenenborgerlaan 171, G.V.521, B-2020 Antwerp, Belgium
All Authors:
Irina Spacova, Mariya I. Petrova, Astrid Fremau, Lore Pollaris, JeroenVanoirbeek, Jan L. Ceuppens, Sven Seys, Sarah Lebeer
2019-02-15 Article
 hth官方网页版中国有限公司
hth官方网页版中国有限公司
